- Home
- Products
- Hardness Testing
- Hardness Test Block
- Yamamoto Metal Hardness Test Block
If you want to find out more about
Yamamoto Metal Hardness Test Block
Talk to us at :
(65) 6749 9697

sales@lfc.com.sg
Hardness Test Blocks Hardness test blocks are required to verify hardness testers to be in good working condition, with a given standard. In order to control various industrial hardness testers, it is important to verify all related factors, including indenters, static and dynamic loads, indentation measurement, and sample pieces. Hardness blocks allow overall control of this coomplicated factors in the field. Therefore, it is imperative that a uniform surface hardness is displayed by all our test blocks, that the main factors of secular change are eliminated and, if possible, that the characteristic of their materials are similar to those of materials in practical use. Yamamoto Scientific Tool Laboratory was established in 1939 by Shoichi Yamamoto. They are the first dedicated manufacturer of standard test blocks in Japan, and has maintained its reputation as the best company in this field.. Material and manufacturing process Yamamoto's blocks are first cut from a plate material to avoid being affected by center segregation. After machining to the required shapes, heat treatment is carefully applied to the blocks to get a stable microstructure and the required hardness level. These steps are taken to maintain a highly uniform surface hardness. Strict quality control of materials must be ensured for each test method. For such cases, a very accurate conversion relationship has been already obtained especially between Shore hardness (HS) , which is the Japanese original standard, and Vickers hardness (HV) values using eutectoid carbon steel. After heat treatment is completed, the blocks are ground, lapped, and then undergo a thorough polishing process, followed by wet buffing to improve measuring precision and achieve the most accurate and consistent hardness available. Care is taken so that the surface is not adversely affected, which could result in surface hardness irregularities, and a routine microscopic structure inspection is performed as required across the finished test surface for possible variations caused in the processes. Each 20-block lot that has undergone heat treatment and other finishing processes is subjected to hardness tests to check for variations in hardness, and to determine reliable, measurement-based reference values. Achieving Precision of Hardness Testers and Hardness Blocks Force, indenter, indentation measurement and movement conditions, etc., should be separately inspected to metrically verify the integrated precision of hardness testers. Industrial adjustments of these conditions focus upon ISO standards. On the other hand, indirect verification of a tester with test blocks is used to integrally verify these respective conditions. It is quite natural, therefore, the uncertainty factor due to the material to be additionally considered, as well as metrical accuracy values. Yamamoto do the utmost in material selection, heat treatment, and other processes to achieve the world’s highest accuracy. Yamamoto Hardness Test Block Characteristics Yamamoto Scientific Tool Laboratory received ISO 9001 Quality System certificate in 1997, issued by Japan Quality Assurance Organization (JQA). It states that the company's quality management system for hardness blocks complies with the requirements of the following standards. The registered certificate No. is JQA -2078 ISO 9001-2000 / JIS Q 9001: 2000. Using the Hardness Test Blocks Normally, the general accuracy of a tester needs to be indirectly verified with blocks for at least the three ranges — high, middle, and low ranges of scales — in which a tester is being used. Routine inspections should be performed with blocks in the high frequency ranges in use. Concerning hardness management with blocks, testers should be directly verified in advance. In this case, at least three readings should be taken, and a X-R controlling method adopted. Measuring locations should be selected over the working surface to represent the hardness of the whole block surface. Serial No. (side), hardness value, and inspection date of hardness blocks are checked against the attached inspection sheet. The warranty period shall be three years from the inspection date, although the blocks are considered to be effective for five years. Flaws and attachments on the front or back surface, as well as re-processing of blocks, are strictly forbidden (This also applies to anvils used). Hardness Test Blocks Durability Secular changes of Yamamoto hardness test blocks are eliminated by a sufficient heat treatment process, regardless of the block type. Due to work hardening near and around the perimeters of indentations, the usable test area is limited, as JIS prescribes it to be 4d (d=diameter of the indentation) as spaces between indentations. To make the maximum use of a block, indentations should be made evenly over the test surface. For this purpose, Yamamoto recommend dividing the working surface (See the figure below). For the durable limits specified in Table 3, reduce the numbers to half if the highest level of accuracy is required.
Hardness Test Blocks
Hardness test blocks are required to verify hardness testers to be in good working condition, with a given standard. In order to control various industrial hardness testers, it is important to verify all related factors, including indenters, static and dynamic loads, indentation measurement, and sample pieces. Hardness blocks allow overall control of this coomplicated factors in the field. Therefore, it is imperative that a uniform surface hardness is displayed by all our test blocks, that the main factors of secular change are eliminated and, if possible, that the characteristic of their materials are similar to those of materials in practical use.
Yamamoto Scientific Tool Laboratory was established in 1939 by Shoichi Yamamoto. They are the first dedicated manufacturer of standard test blocks in Japan, and has maintained its reputation as the best company in this field..
Material and manufacturing process
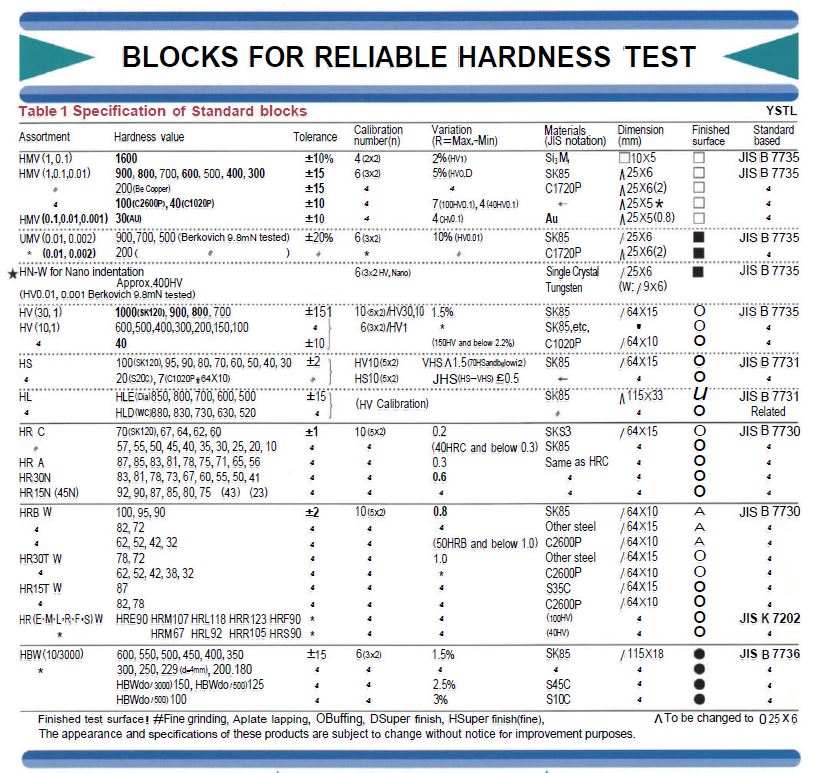
Yamamoto's blocks are first cut from a plate material to avoid being affected by center segregation. After machining to the required shapes, heat treatment is carefully applied to the blocks to get a stable microstructure and the required hardness level. These steps are taken to maintain a highly uniform surface hardness. Strict quality control of materials must be ensured for each test method. For such cases, a very accurate conversion relationship has been already obtained especially between Shore hardness (HS) , which is the Japanese original standard, and Vickers hardness (HV) values using eutectoid carbon steel.
After heat treatment is completed, the blocks are ground, lapped, and then undergo a thorough polishing process, followed by wet buffing to improve measuring precision and achieve the most accurate and consistent hardness available. Care is taken so that the surface is not adversely affected, which could result in surface hardness irregularities, and a routine microscopic structure inspection is performed as required across the finished test surface for possible variations caused in the processes.
Each 20-block lot that has undergone heat treatment and other finishing processes is subjected to hardness tests to check for variations in hardness, and to determine reliable, measurement-based reference values.
Achieving Precision of Hardness Testers and Hardness Blocks
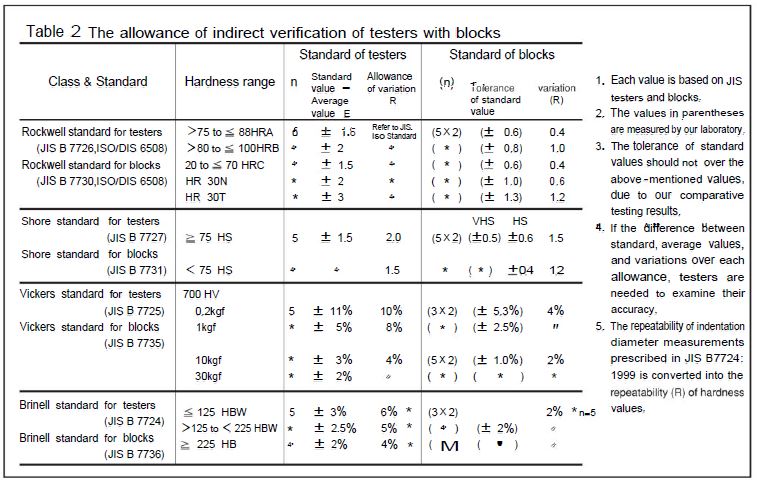
Force, indenter, indentation measurement and movement conditions, etc., should be separately inspected to metrically verify the integrated precision of hardness testers. Industrial adjustments of these conditions focus upon ISO standards. On the other hand, indirect verification of a tester with test blocks is used to integrally verify these respective conditions. It is quite natural, therefore, the uncertainty factor due to the material to be additionally considered, as well as metrical accuracy values. Yamamoto do the utmost in material selection, heat treatment, and other processes to achieve the world’s highest accuracy.
Yamamoto Hardness Test Block Characteristics
Yamamoto Scientific Tool Laboratory received ISO 9001 Quality System certificate in 1997, issued by Japan Quality Assurance Organization (JQA). It states that the company's quality management system for hardness blocks complies with the requirements of the following standards. The registered certificate No. is JQA -2078 ISO 9001-2000 / JIS Q 9001: 2000.
Using the Hardness Test Blocks
Normally, the general accuracy of a tester needs to be indirectly verified with blocks for at least the three ranges — high, middle, and low ranges of scales — in which a tester is being used. Routine inspections should be performed with blocks in the high frequency ranges in use.
Concerning hardness management with blocks, testers should be directly verified in advance. In this case, at least three readings should be taken, and a X-R controlling method adopted. Measuring locations should be selected over the working surface to represent the hardness of the whole block surface. Serial No. (side), hardness value, and inspection date of hardness blocks are checked against the attached inspection sheet. The warranty period shall be three years from the inspection date, although the blocks are considered to be effective for five years. Flaws and attachments on the front or back surface, as well as re-processing of blocks, are strictly forbidden (This also applies to anvils used).
Hardness Test Blocks Durability
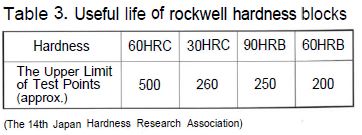
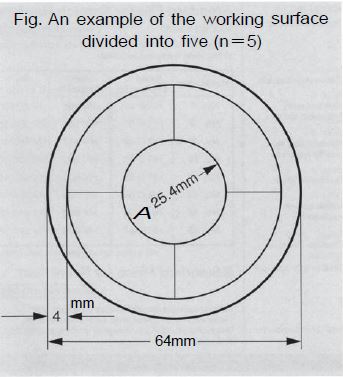
Secular changes of Yamamoto hardness test blocks are eliminated by a sufficient heat treatment process, regardless of the block type. Due to work hardening near and around the perimeters of indentations, the usable test area is limited, as JIS prescribes it to be 4d (d=diameter of the indentation) as spaces between indentations. To make the maximum use of a block, indentations should be made evenly over the test surface. For this purpose, Yamamoto recommend dividing the working surface (See the figure below). For the durable limits specified in Table 3, reduce the numbers to half if the highest level of accuracy is required.
Overview
Built to perfom

Since 1939, Yamamoto Scientific Tool Laboratory Co., Ltd innovates up to 140 kinds of standard hardness test blocks for the metallurgical engineering in the global industry. Yamamoto competencies are known as the world's lowest variances and consistency as low as +0.1 HRC in the HRC 60 range.
Customer value

The highest quality standards from Yamamoto products will deliver you the efficient cost in overall and empower you to take on a job with higher precision on tougher material. Yamamoto’s hardness blocks are ISO 9001 certified, complying with requirement of the ISO standards. The register certificate No. is JQA - 2078 ISO 9001 - 2000 / JIS Q 9001 : 2000
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
Yamamoto Test Block Ordering Guide:
| Rockwell Blocks | Diameter | Nominal Hardness Values | Variation |
NIST Traceable |
| HRA |
64mm |
56, 65, 71, 75, 78, 81, 83, 85, 87 |
+/-0.3 |
No |
| HRB |
64mm |
32, 42, 52 |
+/-0.5 |
No |
| HRB |
64mm |
62, 72, 82, 90, 95, 100 |
+/-0.4 |
No |
| HRC |
64mm |
10, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40 |
+/-0.15 |
Yes |
| HRC |
64mm |
45, 50, 55, 60, 62, 64, 67, 70 |
+/-0.1 |
Yes |
| HR15N |
64mm |
75, 80, 85, 87, 90, 92 |
+/-0.45 |
No |
| HR30N |
64mm |
41, 50, 60, 67, 73, 78, 81, 83 |
+/-0.5 |
No |
| HR15T |
64mm |
78, 82, 87 |
+/-0.5 |
No |
| HR30T |
64mm |
32, 42, 52, 62, 72, 78 |
+/-0.5 |
No |
| HRE |
64mm |
90 |
+/-0.5 |
No |
| HRL |
64mm |
92, 118 |
+/-0.5 |
No |
| HRM |
64mm |
67, 107 |
+/-0.5 |
No |
| HRR |
64mm |
105, 123 |
+/-0.5 |
No |
*Also available for various other ranges of Rockwell , Brinell and Vickers blocks, contact us for your specific spec
Request a Quote
Request A Quote
Please complete the below form to receive further information.